What is the method of improving the power factor? What are the power factors in air conditioners? How do you explain power factor? It has significance only for AC circuit.
For DC circuit, it is not considered for power calculation. Its value is unity for DC circuit and may vary in between zero to one for AC circuit. Power factor is the ratio of two parameters of an electrical circuit. These parameters are KVA (kilo-volt amperes) and KW (kilowatts).
KVA for a single phase circuit is simply the voltage times the. It is an inherent characteristic of loads. Some loads (eg, incandescent lamps) are almost purely resistive, and therefore have a power factor of 1. In AC circuits, the power factor is the ratio of the real power that is used to do work and the apparent power that is supplied to the circuit. The power factor can get values in the range from to 1. When all the power is reactive power with no real power (usually inductive load) - the power factor is 0. Under ideal conditions current and voltage are “in phase” and the power factor is “1.
If inductive loads (motors) are present, power factor less than 1 (typically to can occur). Power is measured in Watts. Power Factor is the ratio of true power to apparent power.
At the simplest level, we could say that an electrical or electronic device’s power factor is the ratio of the power that it draws from the mains supply and the power that it actually consumes. An ‘ideal’ device has a power factor of 1. For the purely inductive circuit, the power factor is zero, because true power equals zero. Here, the power triangle would look like a vertical line, because the adjacent (true power) side would have zero length. The same could be said for a purely capacitive circuit.
If there are no dissipative (resistive). Improving power factor means reducing the phase difference between voltage and current. Find Parts Fast, Same Day Shipping! Trust the Experts at Galco. Keep Your Units Running Smooth.
Protect Against Short Circuits. Shop Fuses, Breakers and Holders. Alternating to Automotive. Level Testing on All Repairs. Month Whole Unit Warranty.

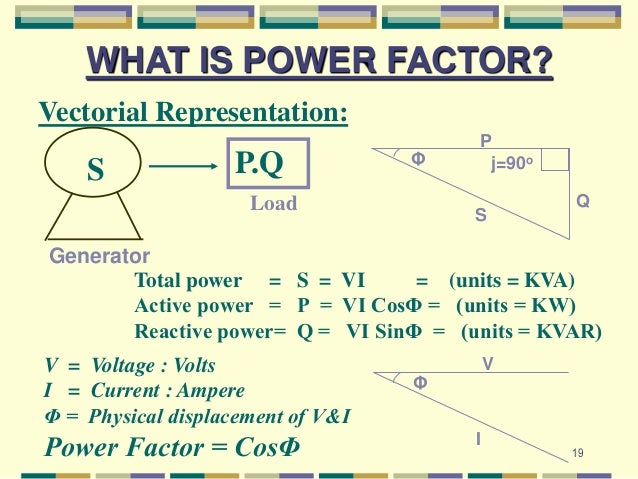
Practically, it should be as close to unity as possible. If power factor is low, following problems are encountered: Effects of low power factor. Apparent power is the total of real power and reactive power.
Simply, it is a measure of how efficiently the load current is being converted into useful work output and more particularly is a good indicator of the effect of the load current on the efficiency of the supply system. Various types of power are at work to provide us with electrical energy. Here is what each one is doing. Working Power – the “true” or “real” power used in all electrical appliances to perform the work of heating, lighting, motion, etc. In this video we learn all about power factor starting at the basics.
We cover, what is power factor , what is good and bad power factor , how to fix bad power factor , what is. Ideally, electrical equipment should present a load that emulates a pure resistor, meaning that the reactive power would be zero. Real Power (kW) is the power that actually powers the equipment and performs useful, productive work. When the resistance of a series RL circuit is increase the circuit becomes more inductive. When the inductance of a series RL circuit increases, angle theta increases.
In a parallel RL circuit, the voltage across each branch is the same. The current is the same at all points in a parallel RL circuit. Free Shipping on Qualified Orders.

Best Place For Test Equipment.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.