
What are the four conditions for perfect competition? What is the difference between perfect competition and monopoly? In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market , also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition , or atomistic competition. In theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hol it has been theoretically demonstrated that a market will reach an equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every product or service, including labor, equals the quantity demanded at the current price. To make it more clear, a market which exhibits the following characteristics in its structure is said to show perfect competition : 1. Large number of buyers and sellers 2. A perfectly competitive market is a hypothetical market where competition is at its greatest possible level.
Neo-classical economists argued that perfect competition would produce the best possible outcomes for consumers, and society. I thought they were the perfect competition because they had the drive and the passion for what they were doing. There was an instance of perfect competition which was indicative of the overall thriving nature of the marketplace we were involved in.
The basic condition of perfect competition is that there are large number of firms in an industry. Each firm in the industry is so small and its output so negligible that it exercises little influence over price of the commodity in the market. Because there is freedom of entry and exit and perfect information, firms will make normal profits and prices will be kept low by competitive pressures. None of the firms are large enough to influence the industry.
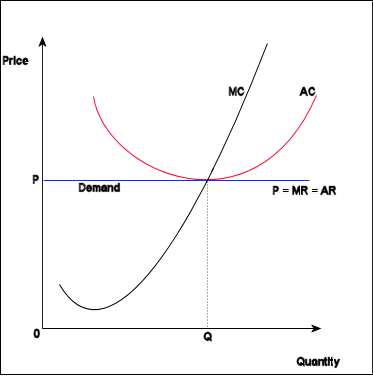
Definition of perfect competition : The theoretical free-market situation in which the following conditions are met: (1) buyers and sellers are too numerous and too small to have any degree of individual control over prices, (2) all. For perfect competition to exist, the sole objective of the firm must be to get maximum profit. It is argued that the model is based on unrealistic assumptions.
The Nations League, for me, is a very attractive competition , a perfect competition , says Spain boss Luis Enrique. Traditional economic theory holds that a monopoly can take advantage of consumers by imposing higher prices than would otherwise be possible under conditions of pure and perfect competition. By this simple reasoning,. Imagine yourself as a street food vendor, selling tacos topped with fried onions, ground meat, cheese, fresh tomatoes and dollops of guacamole and spicy sauce in the main plaza of a town close to the border of Mexico.
The characteristics of a perfectly competitive market include insignificant contributions from the producers, homogenous products, perfect information about products, no transaction costs, and no long-term economic profits. Perfect Competition Defined. In perfect competition , market prices reflect complete mobility of resources and freedom of entry and exit, full access to information by all participants, homogeneous products, and the fact that no one buyer or seller, or group of buyers or sellers, has any advantage over another.
Tutorial includes discussion on profit, lost, marginal cost, average total cost and variable cost. This topic is typically taught in. Free entry and exit conditions. Absence of transport cost.
In a market that experiences perfect competition , prices are dictated by supply and demand. Firms in a perfectly competitive market are all price takers because no one firm has enough market.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.