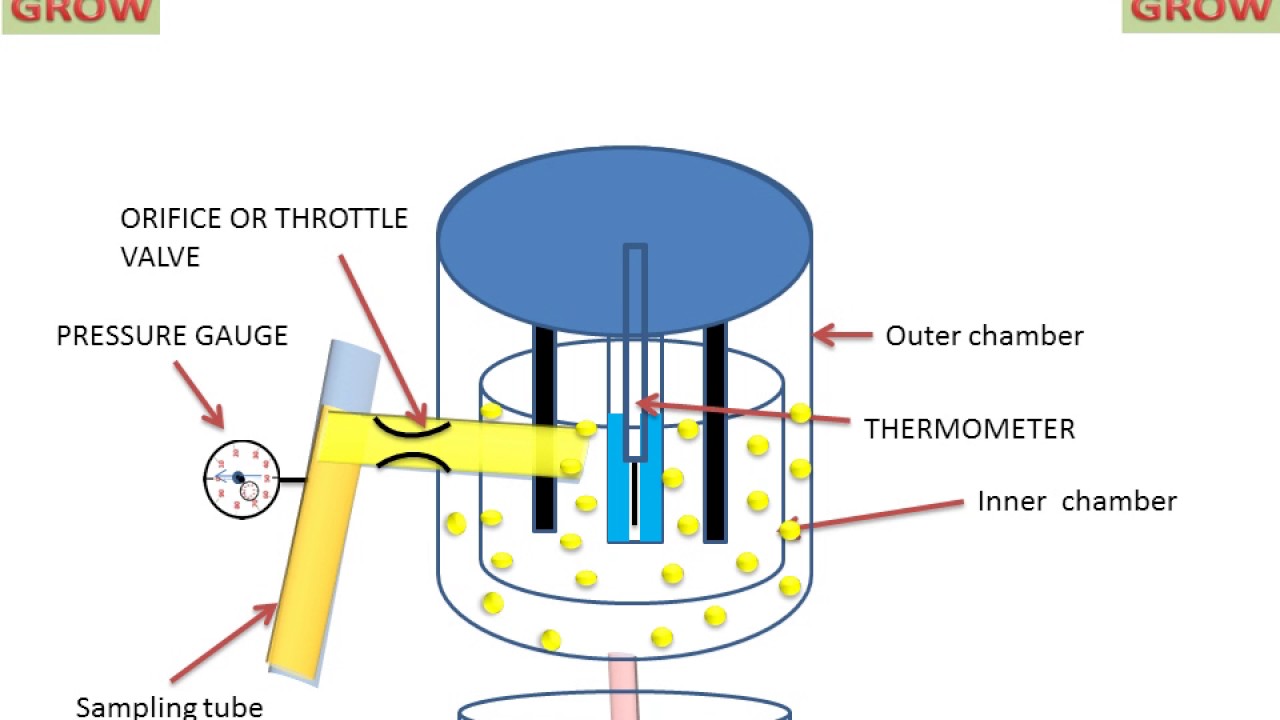
To better understand the theory of the ideal throttling process lets compare what we can observe with the above theoretical assumptions. An example of a throttling process is an ideal gas flowing through a valve in mid position. A throttling can be achieved simply by introducing a restriction into a line through which a gas or liquid flows. This restriction is commonly done by means of a partially open valve or a porous plug.
In thermodynamics , the Joule–Thomson effect (also known as the Joule–Kelvin effect or Kelvin–Joule effect) describes the temperature change of a real gas or liquid (as differentiated from an ideal gas) when it is forced through a valve or porous plug while keeping it insulated so that no heat is exchanged with the environment. Lectures by Walter Lewin. A throttling valve is a device that is used to restrict flow to cause a considerable pressure drop. This in turn can cause a large temperature drop, which is why throttling valves are used in refrigeration devices.
There are many devices that can be considered throttling valves. Adiabatic, steady, throttling of a gas (flow through a valve or other restriction) Figure 2. We wish to know the relation between properties upstream of the valve , denoted by ``1. I am learning basic thermodynamics , and I find it difficult to undestand the principle behind throttling valves , which are used to reduce the pressure of the flow, right? Why velocity being unchanged after passing through the valve ? Could anyone please help? For a throttling valve, why is it that.
Thermodynamic energy analysis of nozzle vs. Throttling devices are another vital parts of all the refrigeration systems and air conditioning systems apart from the compressor, condenser and the evaporator. The refrigerant leaves the compressor at high pressure and temperature and enters the condenser. After leaving the condenser the refrigerant is at medium temperature and high pressure and then it enters the throttling valve.
Why gate valve is not suitable for throttling? Why is the throttling process isenthalpic in nature? What is the throttling process?
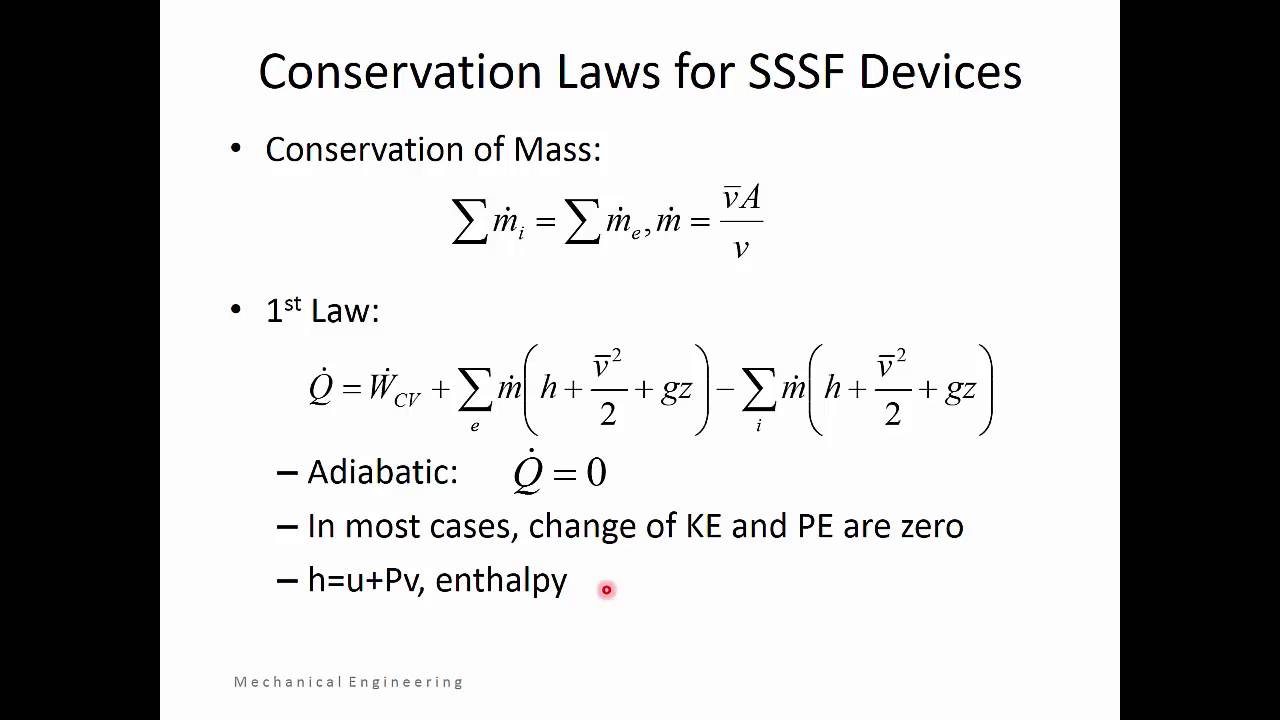
The relation beat heat energy and its conversion to other forms is studied under the branch of physics called. During a throttling process no heat is supplied or rejecte no external work is done and in the case of a perfect gas there is no alteration in temperature. When a fluid expands through a throttle valve or a constricted orifice, the enthalpy before the throttling valve is equal to the enthalpy after throttling.
This is commonly done by means of an adjustable valve , a porous plug, or a capillary tube. They are called throttling devices. Ch Lesson C, Page - 1st Law for Throttling Devices.
The purpose of a throttling device is to reduce the pressure of a flowing fluid. A variety of devices can be used as throttling devices. Valves , porous plugs and capillary tubes are just a few examples. Variable speed operation is an alternative method of controlling the flow of a system. With the throttling valve control metho the pump runs continuously, and a valve in the pump discharge line is opened or closed to adjust the flow to.
Sometimes, fluids flow through a restriction, such as an orifice, a valve , or a porous medium, and a pressure drop occurs adiabatically. I already know that expansion process of fluid through a throttling valve is irreversible process. Entropy of expansion process of fluid through a throttling valve is greater than zero.
So, the plate in the base of a carburetor that opens and closes is a throttling valve.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.