The oil and gas industry, in particular, uses cathodic protection systems to prevent corrosion in fuel pipelines , steel storage tanks , offshore platforms , and oil well casings. Cathodic Protection Program. A critical component of corrosion mitigation, cathodic protection is an electrochemical process to control the corrosion of a metal surface by transferring the corrosion from the protected structure to a more easily corroded metal. On an unprotected pipeline, there are naturally occurring potential variations.
Wherever you go from a minor positive to a minor negative, there is a current flow where galvanic corrosion will occur. A simple method of protection connects the metal to be protected to a more easily corroded sacrificial metal to act as the anode. A properly designed CP system can result in 1 efficiency, increasing the lifespan of structures.
MATCOR has provided expert corrosion prevention services and products for over years, and our corrosion engineering team is ready to provide the industry’s top cathodic protection (CP) system design and specification services for your next project. Virtually all modern pipelines are coated with an organic protective coating that is supplemented by cathodic protection systems sized to prevent corrosion at holidays in the protective coating. However, cathodic protection of a bare structure is usually not cost effective.
Even in a near neutral pH environment a considerable electric current is required to protect a structure. Table shows the required current densities to protect a steel pipeline buried in various soil types. Browse our catalog to see our corrosion prevention products including anodes, backfill, rectifiers and cathodic protection systems. In some cases, CP can even stop corrosion damage from occurring.
Metals, especially ferrous metals, corrode in the presence of oxygen, water, and other impurities such as sulfur. The sacrificial metal then corrodes instead of the protected metal. When the steel becomes cathodic , hydroxyl ions are accumulated around it making it passive for longer time.
Therefore, careful investigation or testing should be conducted before applying cathodic protection to stop pitting attack on aluminum in environments with a natural pH in excess of 8. Figure shows a simple cathodic protection system. The steel pipeline is cathodically protected by its connection to a sacrificial magnesium anode buried in the same soil electrolyte. Impressed current cathodic protection systems have the benefit of using an external power supply to drive current. This makes it possible to protect virtually any structure, regardless of size or current requirements using long life anodes and enough appropriately sized power supplies. It is normally used in conjunction with coatings and can be considered as a secondary corrosion control technique.
Our product range is extensive, as you will see in this website, and our services include a wide variety of cathodic protection engineering and installation offerings. However, his role in the applica-tion of cathodic protection should not be ignored. The designing of cathodic protection systems is rather complex, however, it is based on simple electrochemical principles described earlier in Chapter 2. Corrosion current flows between the local action anodes and cathodes due to the existence of a potential difference between the two (Fig. ). Demands in the cathodic protection market have driven development for better devices and methods, helping to prolong the equipment and pipeline’s life and integrity.
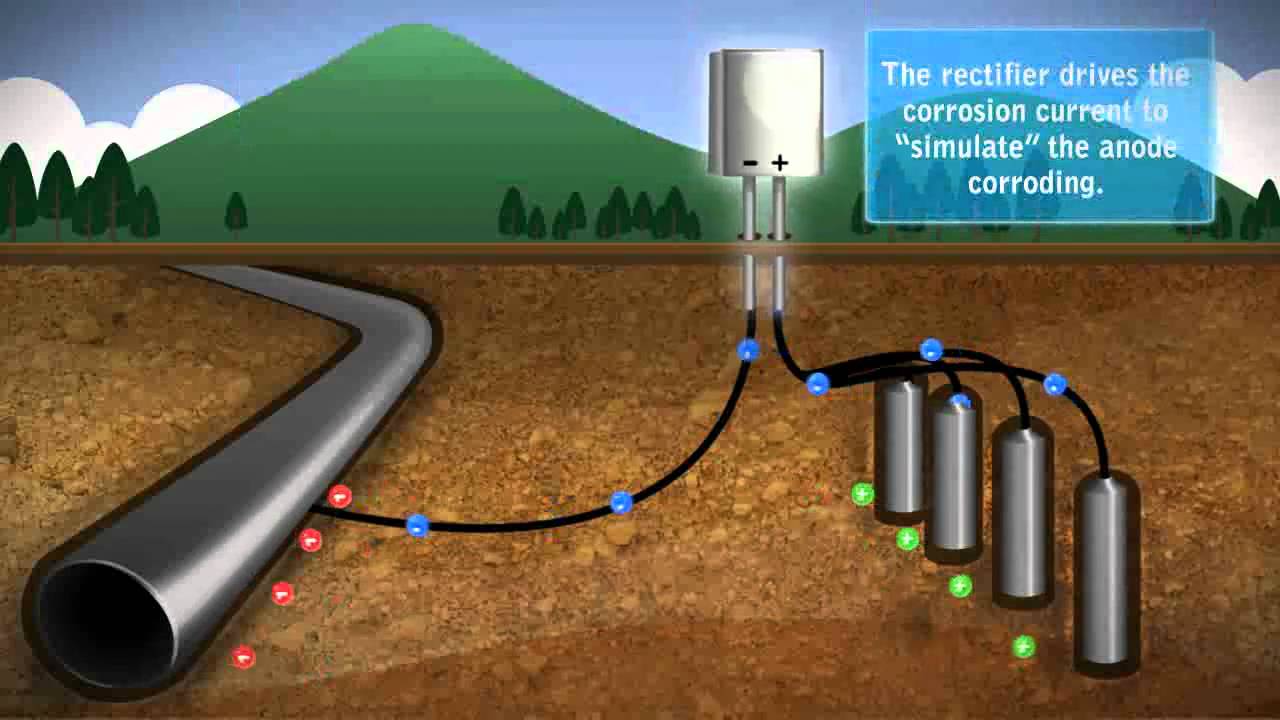
This article provides a brief overview of the corrosion reaction and the role of cathodic protection for both ground storage tanks and elevated water storage towers. Both systems operate by imparting a direct current onto the buried pipeline, using devices called rectifiers. In ICCP, electrons are supplied to the cathodic structure using an external DC power source (also called a rectifier).
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.