Some types of fractures are briefly described in the following paragraphs. A greenstick fracture is an incomplete fracture in which one side of the bone is broken and the bone is bent. A comminuted fracture is one in which the bone is crushed or splintered into many pieces.
Fractures of the forearm! Stress fracture : Bone, like other materials, reacts to repeated loading. Diaphyseal fractures The questions are: 1. Humerus , radius and ulna , femur or tibia ( Fig -1) 2. Proximal end segment , middle segment ( diaphysis ), or distal end segment (Fig -1) 3. Among all different types of fractures , comminuted fracture is a serious one.
The bone will be broken into several fragments. This is a highly complicated injury and usually heals quite slowly. You have this type of fracture when the break is parallel to the long axis of the bone.
Different types of fractures which are based on breaking pattern are. The following figure would illustrate. Salter-Harris type IV fracture Type IV fracture is when there is a fracture through metaphysis, physis, and epiphysis 23. Comminuted fracture - the bone is shattered into many pieces. Compression (crush) fracture - generally occurs in the spongy bone in the spine.
What is a type fracture? In Bucholz R, Heckman J (eds). Byrd HS, Cierny II G, Tebbetts JB: The management of open tibial fractures with associated soft-tissue loss: External pin fixation with early flap coverage. A transverse fracture occurs when a bone breaks at a 90-degree angle to the long axis of the bone.
This typically occurs when a blow transmits a large amount of force directly perpendicular to the bone. There can be either a single break or multiple breaks in a bone. A fracture is a partial or complete break in a bone. A hip fracture is classified by the specific area of the break and the type of break in the bone.
The most common types of hip fractures are: Femoral neck fracture: A femoral neck. There are probably almost as many ways of categorizing bone fractures as there are bones in the body (206!) — pretibial fractures, hip fractures, wrist or colles fractures, and spinal or vertebral fractures, just to name a few — but only a few bones are prone to osteoporotic fractures. The anatomy and biomechanics of pediatric bone differ from that of adult bone, leading to unique pediatric fracture patterns, healing mechanisms, and management. THE BASIC TYPES OF PEDIATRIC FRACTURES , DIFFERENCES FROM ADULTS AND CARE AS A PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIAN. Great toe fractures are treated with a short leg walking boot or cast with toe plate for two to three weeks, then a rigid-sole shoe for an additional three to four weeks.
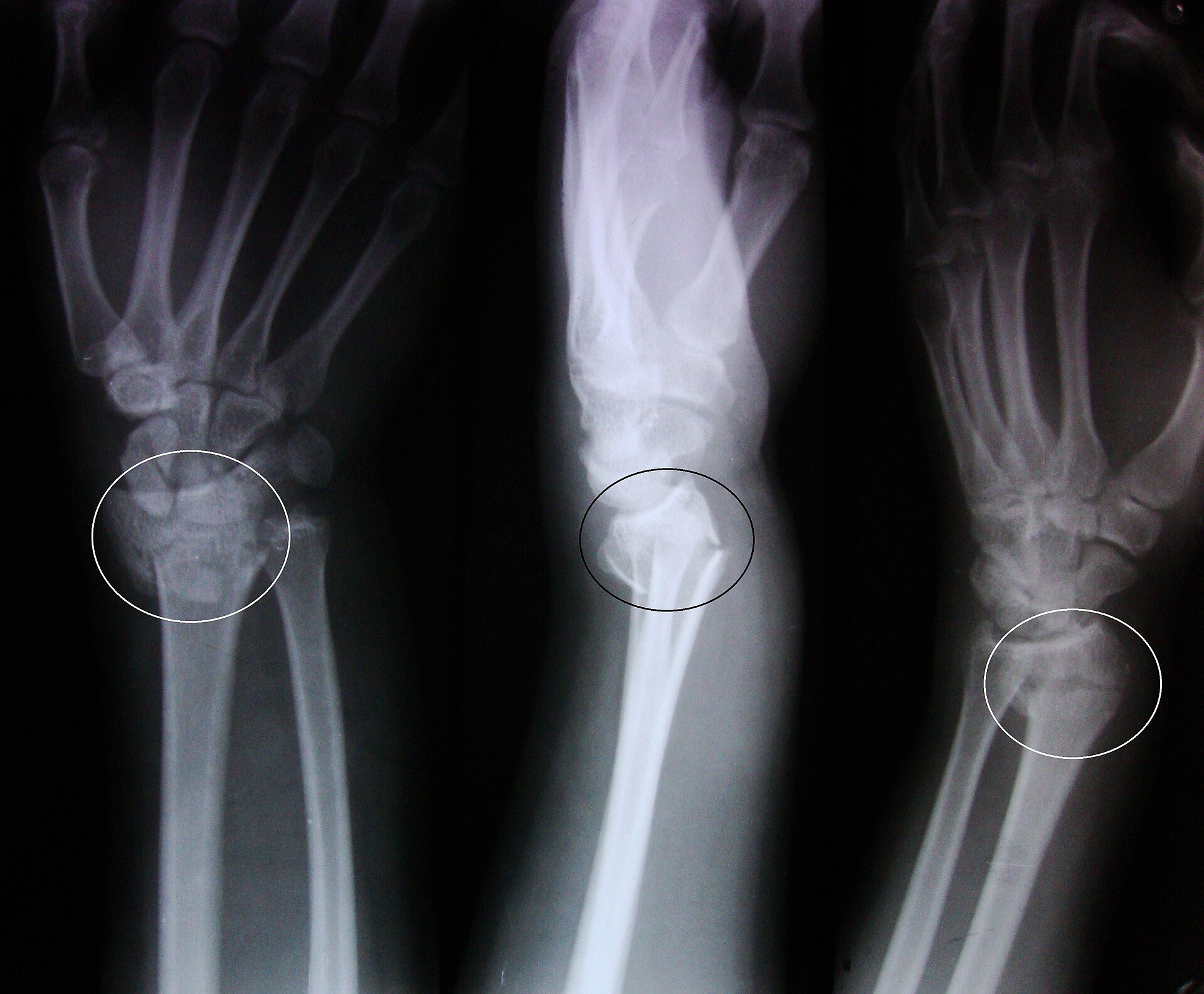
Lesser toe frac- tures can be treated with buddy taping and a rigid-sole shoe for four to six weeks. Distal ulna fracture – this type of fracture involves breaks in both bones of the forearm at the ends nearest your hand. Scaphoid fracture – a fracture that involves the scaphoid bone, one of the eight small bones that make up the carpal bones of the wrist. When direct trauma is applied to a bone, tapping fractures , penetrating fractures or crush fractures are the most common types of fractures encountered. Traction, compressive or rotational fractures result from the indirect application of force to the axis of the bone.
Greenstick fractures are breaks in bones along only one side of the bone caused by a force perpendicular to the bone’s long axis. These fractures , sometimes called midshaft fractures , account for most clavicle fractures and are typically treated without surgery. Group II fractures , which are referred to as lateral or distal fractures , occur furthest from body’s center and near the acromion (a bony extension at the top of the shoulder).
There are many types of fractures , but the main categories are displace non-displace open, and closed. Displaced and non-displaced fractures refer to the alignment of the fractured bone. In a displaced fracture, the bone snaps into two or more parts and moves so that the two ends are not lined up straight.
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.