How do you calculate voltage and current? How is voltage related to current? What is the analogy for voltage and current? Voltage is the difference in charge between two points.
Current is the rate at which charge is flowing. The voltage between two points is equal to the electrical potential difference between those points. When a voltage source is connected to a circuit, the voltage will cause a uniform flow of charge carriers through that circuit called a current. In a single (one loop) circuit, the amount of current at any point is the same as the amount of current at any other point. In particular, we define current at a specific point: the current is the number of coulombs of charge passing by that point per second.
In many cases, a stronger electric force (meaning a higher voltage ) produces a higher current , because the charges are pulled faster toward ground. Currents are the same through all components connected in series. The current through all parts (battery, resistor and LED) is 20mA. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. When talking about alternating current (AC) there is a difference between instantaneous voltage and average voltage.
I is the current through the conductor in units of amperes, V is the voltage measured across the conductor in units of volts , and R is the resistance of the conductor in units of ohms. Voltage (V) or Potential Difference (p.d.) is a measure of the Energy transferred per Charge Carrier between two points. Objects are moving, chemical reactions are taking place, temperatures are increasing and decreasing. This abundance of perpetual activity is bound to the concept of energy. In other words, current is the rate of flow of electric charge.
Electric power is the rate, per unit time, at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Some countries have more than one voltage available. For example, in North America most sockets are attached to a 1V supply, but there is a 2V supply available for large appliances. Often different sockets are mandated for different voltage or current levels.
Voltage , frequency, and plug type vary, but large regions may use common standards. Basic electrical quantities: current , voltage , power. This is the currently selected item. Resistivity and conductivity.
Analyzing a resistor circuit with two batteries. As you know, there are two types of combinations in a circuit, they are series and parallel connections. Parallel circuits are also known as current divider circuits because, in these circuits, the current is divided through each resistor.
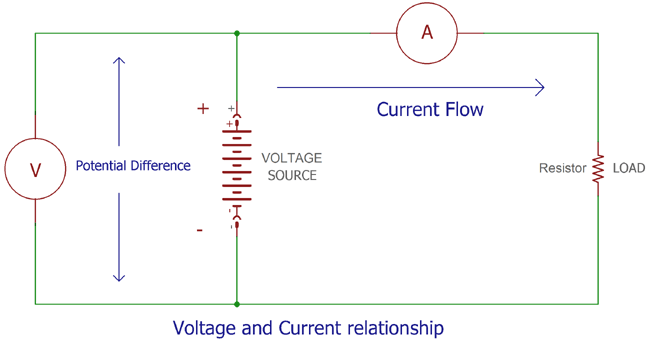
Whereas, series circuits are known as voltage divider circuits because here voltage is divided across all the resistors. Voltage, also called electromotive force, is the potential difference in charge between two points in an electrical field. Explanations of the units Amps, Volts, Coulombs per second and Joules per Coulomb. One ohm is defined as the resistance which allows the current of one ampere under a potential difference of volt. Voltage definition is - electric potential or potential difference expressed in volts.
How to use voltage in a sentence.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.